Emphasis on All Material Issues for Sustainability in All Dimensions
CP ALL Plc. and its subsidiaries (“the Company”) has continuously published its sustainability report for the 8th consecutive year, serving as a communication channel for performance under sustainable development policies and strategic frameworks, informing all stakeholder groups. This is inclusive to the Company’s, environmental, social, and governance and economic dimension.
Published performance cover the period of 1 January to 31 December 2O23, encompassing 3 key business units. In 2O23, the Company’s net revenue was at 921,187 million Baht. Additional information regarding subsidiaries is disclosed in on page 2 of 2O23 annual report.
This report’s content was established upon the foundation that is the Company’s overview operation and material topics affecting 3 dimensions of sustainability, all according to every stakeholder group’s perspective and key impact assessment. The reporting framework aligns with international sustainability reporting standard 2O22 edition (GRI Sustainability Reporting Standards 2O21: GRI Standards 2O21) and The Food Processing Sector Supplement. Simultaneously, the Company assigned an internationally reputable and credible third-party, LRQA (Thailand) Limited to verify the report.
In 2O23, the data set reviewed comprises GRI 2-26, GRI 2-27, GRI 3-1, GRI 3O2-1, GRI 3O2-3, GRI 3O3-3, GRI 3O3-4, GRI 3O3-5, GRI 3O5-1, GRI 3O5-2, GRI 3O5-3 other indirect (Scope 3) GHG emission (Purchased goods and services, Capital goods, Fuel and energy related activities, Upstream transport and distribution, Waste generated in operations, Business travel, Downstream transport and distribution, Use of sold products, End-of-life treatment of sold products only) GRI 3O5-4, GRI 3O6-3, GRI 3O6-4, GRI 3O6-5, GRI 3O8-1, GRI 3O8-2, GRI 4O3-9, GRI 4O3-1O, FPSS FP6, FP7, GRI 4O5-2, GRI 414-1, GRI 414-2
Retail business Convenience store

Convenient Store Service
Wholesale and Retail businesses Service

Wholesale Service

Retail Service
Others

Financial Service
Information Service

Food, Bakery, and Ready-To-Eat Meals Service

Marketing Media Services

Educational Service

Logistic Management Service
Determining the Report’s Content
The Company developed the report by considering and assessing significant impacts to every group of the Company’s stakeholders, addressing both positive and negative impacts. Considerations are also given to sustainability material topics from internal factors in business operations, and external factors of global trends among peers, including world-renown sustainability indices as the Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI), Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) This ensures the Company’s sustainability performance disclosure is in accordance with the 8th reporting principles, as follows:
| Global Reporting Initiative Standards (GRI) | |
|---|---|
| 1. Accuracy | Disclosed data accuracy |
| 2. Balance | Balance of performance reported, both positive and negative |
| 3. Clarity | Comprehensibility for all stakeholder groups |
| 4. Comparability | Data compatibility to illustrate performance trend |
| 5. Completeness | Data completeness and comprehensiveness |
| 6. Sustainability context | Balance of performance reported, both positive and negative |
| 7. Timeliness | Scope of reporting timeline |
| 8. Verifiability | Verifiability |
Material Topics
The Company maintains the process and step for Materiality Assessment which considers Impact Materiality associated to stakeholders, consisting of 4 main steps as follows:
| Identify and assess impacts on continuously basis | |
|---|---|
| 1. Understand the organization’s context | Consider business operation activities to define stakeholder groups throughout the value chain and determine sustainability issue links encompassing environmental, social, and governance and economic dimensions, including human rights issues associated t |
| 2. Identify actual and potential impacts | Identify Sustainability Context and Impact, both Actual & Potential Impact issues through analyzing Impact Materiality covering social and environmental issues to elicit Positive & Negative Impact along with considering Short Term & Long-Term Impact and resilience evaluation from Irreversible & Reversible Impact. Sustainability issues are considered from the business operations characteristics and organizational context. |
| 3. Assess the significance of the impacts | The Company reviews sustainability issues identified as posing various impacts into consideration in conjunction with business characteristics and organizational context. Processes for Impact Materiality evaluation is conducted through workshop format with representation from all 8 groups using criteria for severity scale assessment, scope, capability for reversibility, and likelihood of impact towards stakeholders, to prioritize sustainability issues. |
| Determine material topics for reporting | |
| 4. Prioritize the most significant Impacts for reporting |
The Company revises Impact Materiality results from the organized workshop to determine significant sustainability issues. The issues taken into consideration along with comprehensive appraisals enable the determination of linkages and contextual appropriateness within organizational business operations for Material Testing. A select group of professionals with knowledge and abilities specific to convenience stores and retail business, cash-payment and self-service wholesale business and other relevant business are tasked with determining connections and global trends, including ESG sustainability indices from Morgan Stanley Capital International (MSCI), the Dow Jones Sustainability Indices (DJSI), Global Trend and Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), etc. Results from significant sustainability issues testing are presented to senior management representatives and the Board of Directors to ensure prioritization. Considerations for stakeholder influence and decisions in conjunction with economic, social, and environmental impacts inclusive of human rights are highlighted. |
Assessing Impacts of Material Topics
| Material Topics | Impacts on Society/Environment and business value drivers |
|---|---|
| Climate Resilience |
Efficient utilization of resources with technological integration in tandem with the Company’s circular economy strategy enables reduced energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions in addition to satisfying societal expectations regarding climate challenges. As a result, this approach increases business opportunities with suppliers in terms of climate change aspects, fosters trust among investors and develops collaboration with the government sector. Failure to recognize climate change impact arising from a company’s business activities potentially increases operating costs due to climate change impacts and ensuing raw material price fluctuations, supply chain disruptions, and high operating costs incurred from climate change response inclusive of fees, carbon taxes, and administrative costs to maintain business continuity. In addition, conducting business without considering the impact on global climate change may affect lifestyle, health, and safety of all stakeholders throughout the value chain. Long-term impact includes air pollution which affects health and safety of workers and surrounding communities, drought and flood impact on suppliers, and capability to deliver products and raw materials. |
| Efficient use of resources and Energy |
Efficient energy management, clean energy technology development, and renewable energy assists in climate change impact reduction while increasing business opportunities and confidence among investors. Inefficient energy management may result in increased production costs thus decreasing profits and community rights violations in relation to distribution of clean water access in communities surrounding company business operations. |
| Sustainable packaging management |
Operating both a retail and wholesale business requires consideration for environmentally friendly packaging selection, usage reduction, take-back systems and efficiently recycling to enable proper organizational plastic waste management, added value, production cost reductions, and both intra- and interorganizational stakeholder participation. Without considering packaging properties inclusive of recyclability and materials decomposition, discarded plastic waste remains in the environment in large quantities thus impacting ecosystems, human food safety issues, various health concerns, and operating costs in addition to organizational reputation and image. |
| Sustainable waste and surplus food management |
Product distribution management and efficient food waste management assists food waste reduction occurring from overproduction and food wastes arising from transportation, distribution and storage. Waste management which converts food waste into alternative raw materials allows economic value creation, food waste alleviation, and company operating cost reduction. Ineffective management results in increased food waste quantities and greenhouse gas emissions which negatively impacts ecosystems and natural resources in addition to surrounding community health and wellbeing. Company operating costs are also impacted with inappropriate waste management. |
| Good Health and well-being |
Management throughout the process of sourcing raw materials, production, and distribution requires awareness of delivered product in terms of maintaining safety and uphold standards, a factor affecting increasing business opportunities. Additional matters relevant to delivering nutritious products include additional access to health and well-being services within the community. A lack of awareness in consumer safety may pose risks in delivering products harmful to health. Long-term negative impact on consumers from diseases caused by lifestyle behaviors (Non-Communicable Diseases: NCDs) may result in lawsuits and damage to organizational reputation and image. |
| Social Impact and economic contribution |
Conducting socially responsible business supports job creation, provides community well-being, builds good community relationships, and increases community acceptance of Company activities. Moreover, the government and private sectors emphasizes support for all societal groups in equal access to products and services, a means to reduce inequality, improve life quality and increase civil well-being. In the even where the Company conducts activities affect the community, life quality in surrounding communities would be violated, community-organization conflicts would arise, Company license to operate may be declined, and Company image may be tarnished. |
| Corporate Governance and Anti-Corruption |
Good corporate governance enhances organizational business operation efficiency, competitiveness and builds confidence. This approach attracts investors and employs critical guidelines which assist in business value creation. The Company reviews operations displaying inefficient corporate governance, non-transparent activities, and disregard for morality, ethics, and human rights. The mentioned actions affect business competitiveness, reduces stakeholder confidence towards the organization, reduces investor interest, while increasing human rights and legal violations risk. |
| Occupational health and safety & Labor practices |
Security management and effective occupational health may reduce work-related accident incidences, increase operational capabilities, and boost Company confidence among employees and suppliers. Meanwhile, poor occupational safety and health management could cause loss of life and property, leading to disruptions in production processes and decreased productivity from lab capital stock. Other negative impacts include lower employee morale, fines, and tarnished Company credibility and reputation. In addition, 7-Eleven store’s customer and property safety may be impacted |
| Human capital development |
Leadership and human resources development allow the creation of vital skills among employees at all levels, creates technological and digital platform comprehension which increases operational potential, increases employee engagement, affects business operation efficiency, and improves business resilience to market changes. Ineffective personnel development processes representing inequality and discrimination create human rights violation risks. Instances of mentioned grievances include female employee salaries lower then male employees, etc., which negatively impacts organizational growth and decreases the Company confidence among employees and suppliers. |
| Responsible supply chain management |
Appropriate supply chain management could reduce risks associated to cost, raw material supply shortage, inventory, and human rights violations while instilling confidence in the Company among employees and suppliers. This approach increases the ability to generate profits. Inefficient supply chain management with disregard to human rights pose risks associated to business disruption, poor quality products, delayed deliveries to consumers, increased production and transportation costs, Company reputation and image, and environmental and social costs imposed by societal and investor expectations. |
2023 Materiality Topics
Environmental
7 Go Green
– Climate Resilience
– Efficient use of resources and Energy
– Sustainable Packaging Management
– Sustainable Waste and Surplus Food Management
Social
7 Go Together
– Social Impact and Economic Contribution
– Good Health & Well-being
Governance and Economic
7 Go Right
– Corporate Governance and Anti-Corruption
– Occupational Health and Safety & Labor Practices
– Human capital development
– Responsible Supply Chain
Assessment of sustainability issues “Double Materiality Assessment”
In addition to the Impact Materiality process that identified key material topics in 2O23, the Company conducted a Double Materiality Assessment together with the risk management department. This assessment evaluated both Impact Materiality and Financial Materiality, considering the impacts of the Company’s operations on society and the environment alongside the social and environmental factors affecting the Company’s business performance. The results of these assessments shall be used to guide business operations, develop strategies, and drive future initiatives of the Company.
Sustainability issue assessment “Double Materiality Matrix” results
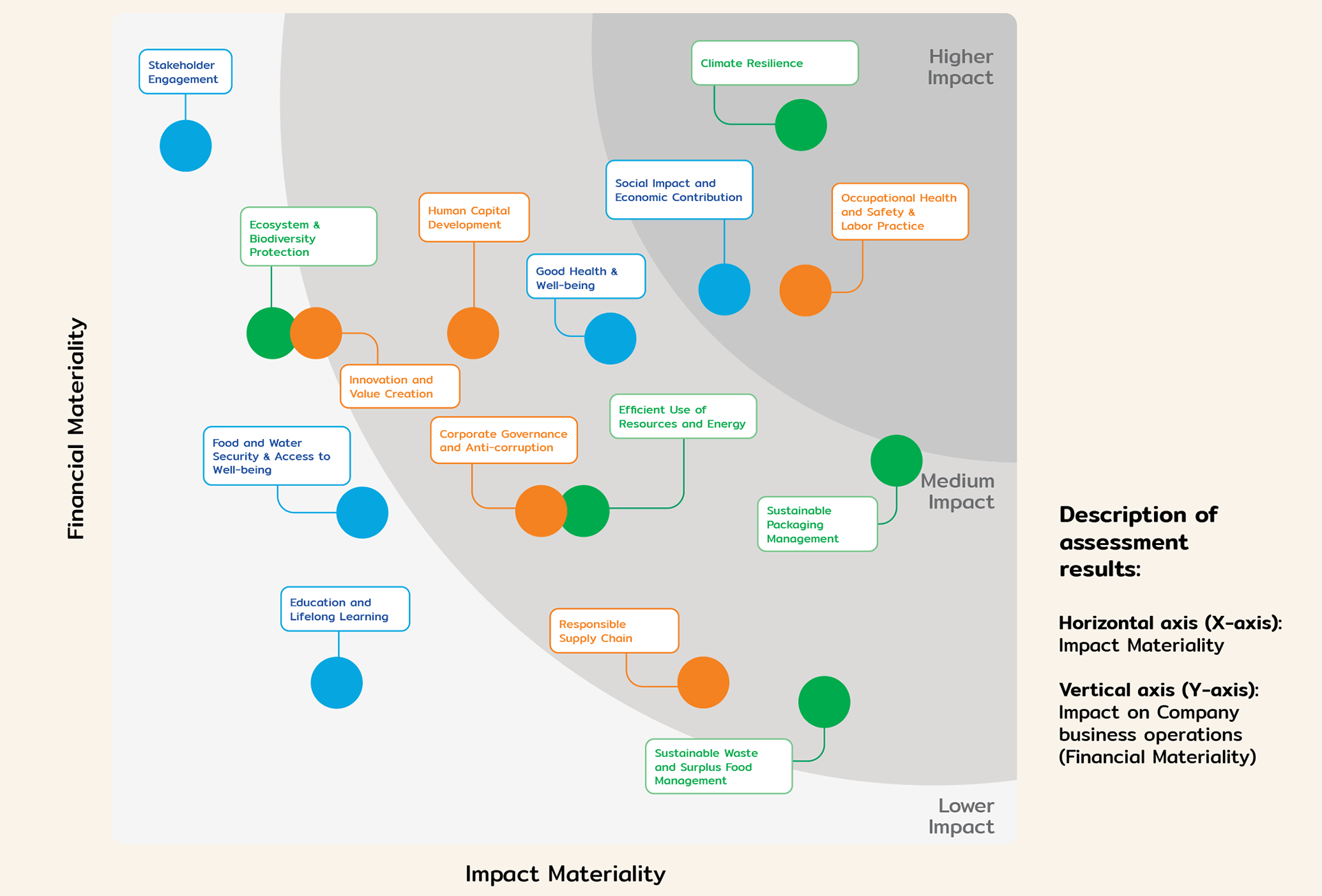
Sustainability Dimension
Impact level for application in business operations
|
Lower Impact |
Considered operations (Areas to monitor): Sustainability issues which require Company compliance to business ethics and code of conduct without adjusting business strategies. |
|
Medium Impact |
Evaluate operational processes and management (Enablers): Sustainability issues which companies should evaluate respective operational and management processes for future business strategies development and modifications. |
|
Higher Impact |
Initiate strategic difference (Differentiators): Sustainability issues which companies should focus on and accelerate operations to satisfy market demands while maintaining consistency with organizational goals and business strategies. |
Contact Information
Should you have any query or wish to request any further information related to this report, please contact: Corporate Sustainability Management Division, Sustainable Development Function
CP ALL Public Company Limited
Headquarter: 313 CP Tower, Floor 24, Silom Rd., Silom, Bangrak, Bangkok 10500
