Management Approach
Effective risk and crisis management is a crucial mechanism for long-term financial planning and organizational resilience. It helps identify potential risks and issues that may impact the organization. The company’s risk management process begins with a review of the organization’s strategic plans and business objectives, along with an analysis of materiality topics. This enables the development of a risk management framework and the identification of key risks to the business. The framework encompasses four dimensions: business risk, sustainability risk, emerging risk, and black swan risk. Additionally, the company implements effective prevention and mitigation measures to drive the organization towards its goals and create value for all stakeholders.
Risk governance framework
The company has established a Risk Management Committee responsible for setting risk management policies and plans, as well as determining the organization’s risk appetite. The risk management and internal audit departments serve as members of the committee, driving effective risk management operations under sound corporate governance and aligned with organizational objectives. The committee is also responsible for reporting risk management performance to the audit committee and the board of directors twice a year. This allows for a review of the risk management process, as well as the identification of opportunities to enhance efficiency and mitigate risks more effectively.
Corporate Risk Management Structure
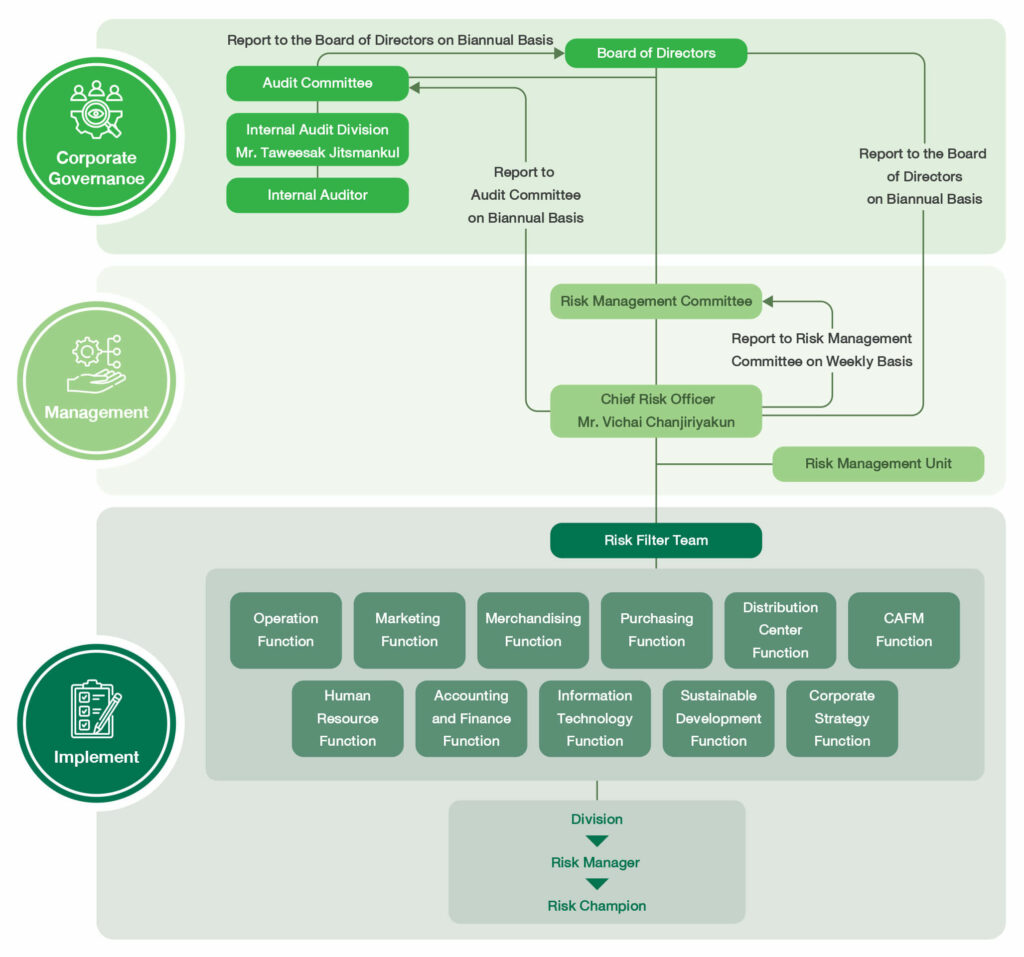
The Company established a Risk Management Committee to determine risk management policies, plans, and acceptable risk appetite in conjunction with the risk management department and regulatory agencies. This approach enables effective risk operations and alignment with good corporate governance principles. The Risk Management Committee is also tasked with reporting operational performance to the Audit Committee and the Board of Directors twice a year for risk management review, follow-ups, and resolution of identified organizational risk issues. The mentioned practices support an internal control mechanism, enable efficient risk monitoring, and ensure conformity to international standards.
In addition, the Risk Management Committee has conducted self-assessments and group assessments using an assessment form adapted from the Thai Institute of Directors Association in conjunction with the charter. In 2024, the Risk Management Committee received an excellent performance score for 94% of operations and a good performance score for 6% of operations.
1. Board level risk oversight
The board of directors oversees the risk management system, providing independent recommendations for critical risks. It also establishes a risk management policy, considering significant risk factors, including risk management guidelines and monitoring the performance of risk mitigation plans.
2. Operational risk management functions
Roles and responsibilities in risk management
| Level | Responsible | Roles and responsibilitie |
|---|---|---|
| Third Line | Internal Audit Division / Internal Auditor | 1.Monitor, review, and audit against risk-based standards 2.Ensuring the organization has appropriate risk management practices |
| Second Line | Risk Management Committee (RMC) | 1.Identify and assess significant business risks, including strategic, financial, operational, regulatory, and reputational risks. Propose risk mitigation strategies and develop policies and procedures to manage these risks effectively. Provide recommendations to the board and management on risk management practices 2. Develop a comprehensive risk management plan and processes to achieve the organization’s objectives and goals. 3. Oversee and support the risk management program. Monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the risk management framework throughout the organization. Review and update risk management policies, systems, and plans on an ongoing basis to ensure they remain appropriate to the changing business environment. 4. Communicate with the audit committee regarding significant risks to assess the adequacy of the company’s internal control system. 5. Report the results of risk assessments and risk mitigation efforts to the board of directors at least twice a year. In case of any significant events that could materially impact the company’s financial position or operating results, the board of directors shall be informed immediately. 6. Perform such other duties as may be assigned by the chairman of the board. |
| First Line | Risk Filter Team (Risk Manager , Risk Champion , Risk Owner) | |
| -Risk Manager | 1. Define a risk management strategy to maintain risks at an acceptable level, known as Risk Acceptance, to achieve departmental objectives and align with the organization’s goals 2. Review significant departmental risks, monitor them, and assign Risk Owners to take necessary actions. 3. Effectively communicate departmental risks to management and employees to promote a culture of identifying new or emerging risks 4. Appoint a departmental Risk Champion to coordinate with the enterprise risk management function and ensure compliance with established policies. 5. Propose improvements to enhance the risk management process, aligning it with the department’s mission |
|
| -Risk Champion | 1. Manage the identification, review, analysis, and reporting of risk profiles for relevant departments or units. Present these findings to the department’s senior management (Risk Manager) for consideration and subsequent presentation to the Risk Management Committee 2. Support the development of departmental/unit Business Continuity Management (BCM) plans, ensuring alignment with the organization’s and business group’s BCM plans 3. Coordinate with the Risk Management Committee to ensure compliance with established risk management policies 4. Execute risk management activities as assigned by the department’s Risk Manager |
|
| -Risk Owner | 1. Manage and control departmental risks, as assigned by the Risk Manager, to maintain them at an acceptable level 2. Review, assess, and document departmental risks in relevant risk registers in collaboration with the Risk Champion 3. Identify, monitor, and report significant risk indicators to the Risk Manager on a regular basis 4. Report on the progress of assigned risk mitigation plans and maintain emergency response plans 5. Participate in various activities as assigned by the Risk Manager and Risk Champion |
|
Risk Management Framework
CP ALL has adopted the international standards COSO ERM:2017 and ISO 22301:2012 as its Enterprise Risk Management Framework to effectively address evolving business needs within a sustainable risk management and crisis management framework for CP ALL Public Company Limited and its subsidiaries
Risk and Incident Management Framework for Sustainable Business Operations
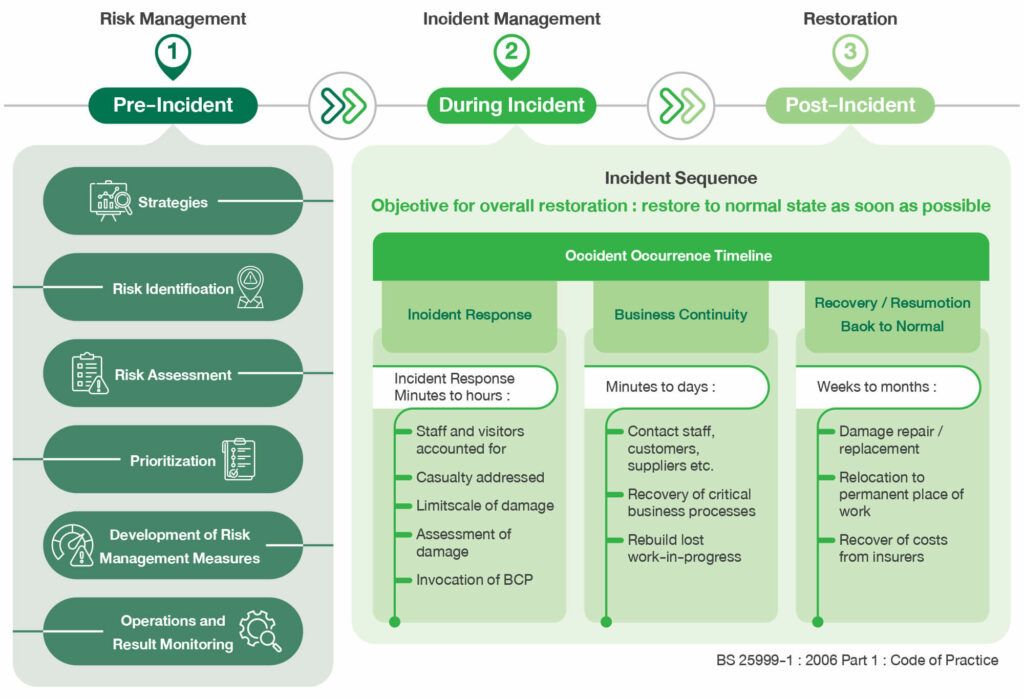
Risk Management Process
The company has established a framework for enterprise risk management and crisis management, encompassing enterprise-wide risk management, operational risk management, and effective communication to all employees. A risk management plan has been developed to address potential risks that could impact the organization’s operations and objectives. Risk prioritization is determined through a risk matrix analysis, considering the likelihood and impact of each risk, including the potential for fraud and corruption. Key risk performance indicators (KPIs) have been established, along with appropriate recovery plans to ensure the organization’s long-term sustainability.
Risk identification
Risk identification is the initial and crucial step in the risk management process. It involves identifying potential events, circumstances, or factors that could impede the achievement of objectives, cause harm, or result in losses to an organization, project, or activity. A risk assessment committee, comprising experts from diverse fields such as communications, retail operations, law, human resources, facilities, location, cybersecurity, data privacy, government relations, and occupational health and safety, is tasked with this responsibility.
Through brainstorming sessions with various departments and analyzing the potential risks associated with significant projects and activities, the committee identifies risks. To ensure comprehensive risk identification, the committee utilizes the Universal Risk Area (URA) framework. This framework provides a structured approach to understanding high-risk areas and identifying the types of risks that may arise within those areas. Additionally, the Universal Risk Project Area (URPA) framework is employed for project-specific risk identification, considering both internal and external factors as well as future trends that may impact organizational objectives. The types of risks identified encompass:
- Business Risks: Including strategic, operational, financial, and compliance risks
- Sustainability Risks: Environmental, social, and governance risks
- Emerging Risks: New and unforeseen risks that may arise
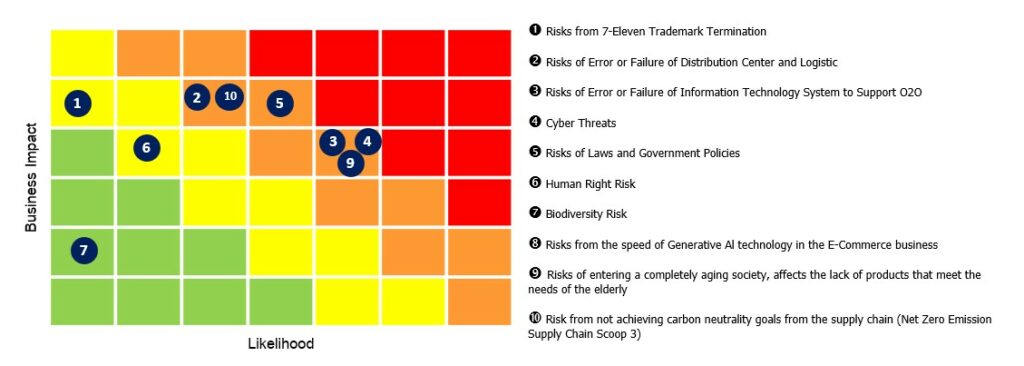
In 2024, the organization was able to identify and compile a comprehensive risk register for various projects and activities.
| Key Risk | ESG Risk | Emerging Risk | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risk from 7-Eleven Trademark Termination | ✓ | ||
| Risk of Error or Failure of Distribution Center and Logistic | ✓ | ||
| Risk of Error of Failure of Information Technology System to Support O2O | ✓ | ||
| Cyber Threats | ✓ | ||
| Risk of Laws and Governance Policies | ✓ | ||
| Human Right Risk | ✓ | ||
| Biodiversity Risk | ✓ | ||
| Risks from the speed of Generative AI technology in the E-Commerce business | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Risk of entering a completely aging society, affects the lack of products that meet the needs of the elderly | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Risk from not achieving carbon neutrality goals from the supply chain (Net Zero Emission Supply Chain Scope 3) | ✓ | ✓ |
Risk Review / Risk Assessment
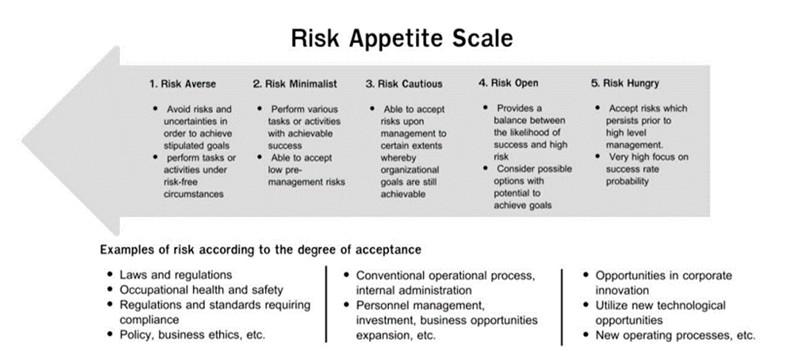
The Risk Management Committee has established a risk assessment framework that considers the likelihood and impact of potential risks and create a risk rating scale from low to high using colors to indicate risk levels. Each risk owner is assigned to analyze the probability and impact levels using a risk matrix. The company prioritizes risks through assigning the respective Risk Owner to analyze the risk Probability Rating Scale and Impact Rating Scale utilizing a Risk Matrix with principles and guidelines described in the following text.
Risk Matrix
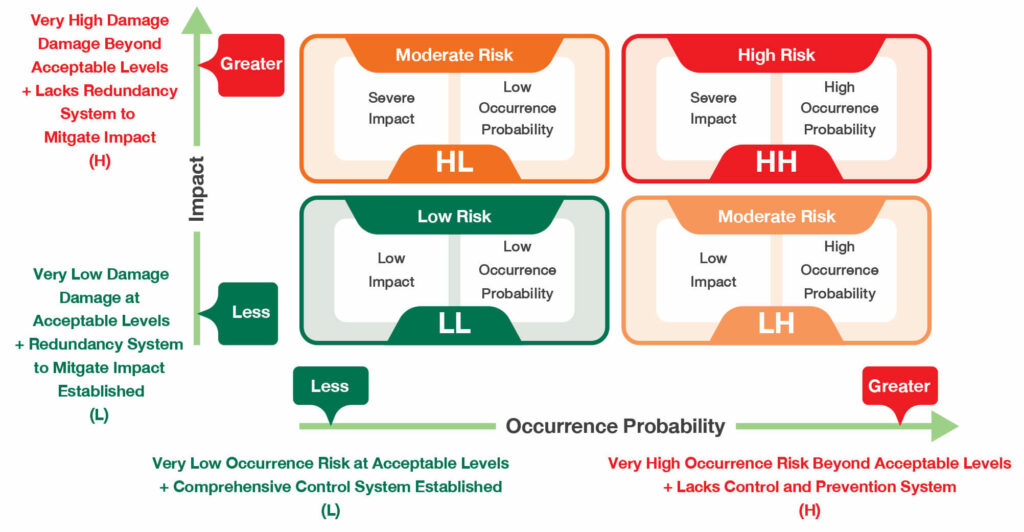
Translate into English and create a risk rating scale from low to high using colors to indicate risk levels.
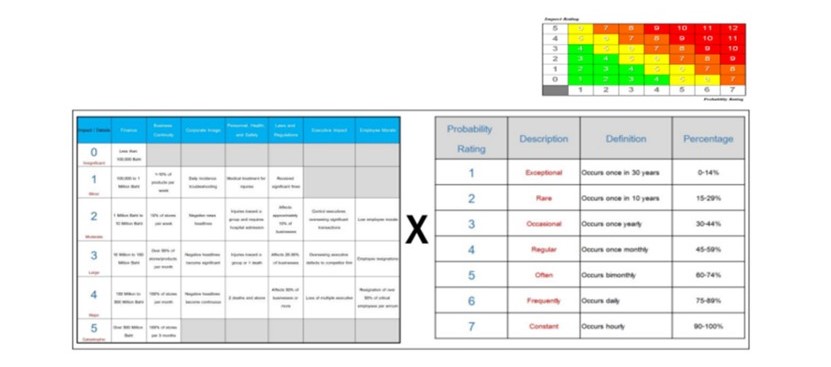
Define the organization’s maximum acceptable risk levels in various areas, such as finance, operations, and reputation, to provide a framework for the risk assessment team to make decisions about the organization’s risk tolerance. This will help identify key risks that are relevant to the organization, ensure alignment with the organization’s strategy, and drive decision-making in a consistent direction.
Risk owners, in collaboration with the risk management unit, conducted a risk analysis using a risk matrix as a tool to assess risks. This involved evaluating the likelihood or probability of a risk occurring, compared to the severity or impact of the risk if it does occur. Risks were prioritized using a company-defined probability rating scale and impact rating scale. A risk score was assigned to each risk, and a maximum risk appetite level was established for the organization. This ensured that risk management activities aligned with the organization’s objectives, goals, and relevant laws, regulations, and standards, considering the business continuity and disaster recovery plans.
In 2024, the company reviewed, assessed, and prioritized its organizational risks.
Defining risk management measures
The organization will implement a risk management framework where significant risks are identified and assigned to appropriate organizational levels. Risk owners will develop risk mitigation plans, emergency response plans, or business continuity plans based on the principles of the 4T+1P framework: Treat, Transfer, Terminate, Example measures as follows:
Business Risk
2. Risk of Error or Failure of Distribution Center and Logistic
| Impact | Likelihood | Risk Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Moderate | MM |
| Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| The Company recognizes the importance of its distribution center management system and technological tools to support its new services and distribution channels such as online shopping, online to offline (O2O) services, and parcel delivery services. Most of the products sold in 7-Eleven stores nationwide are delivered from the Company’s many distribution centers, located in Bangkok and other provinces across the country. This network of distribution centers helps small and large manufacturers to safely deliver their products to operating 7-Eleven stores 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Therefore, the distribution centers play a vital role in 7-Eleven’s business in distributing products to stores across the country in a correct, complete and timely manner. Errors or problems at the distribution center and disruption of transport route due to floods, fire, communication system and information technology failure, pandemic, severe accidents, or any force majeure from the supply chain system from the manufacturer to distribution centers and then delivery at the stores, will have an adverse impact on the sales of all 7-Eleven stores and business opportunity, and may negatively affect the Company’s operating performance. |
The Company regularly reviews and optimizes distribution channels and distribution centers for different product types for optimal performance and to have sufficient space to support sales growth from its stores and new online businesses both domestic and abroad. The Company has also issued internationally recognized policies and practices for its trade partners, communicated through training and risk assessments. Results from risk assessments and audits are used for future developments and to find new opportunities for growing sustainably together with trade partners. In addition, the Company also regularly monitors the preparedness of its equipment, personnel, and transportation routes to deal with disruptions in distribution. In the case that a new distribution center needs to be set up, the Company will select locations that are both safe and efficient for delivering products to its stores. This includes locations within stores’ perimeters, spread throughout various provinces nationwide. With this strategy, the Company is confident that it can reduce risk factors related to distribution centers as it supports the growth of new stores and businesses in the future. The Company has prepared and practiced the Incident Action Plan and conducted drill regularly planned to be ready to deal with various crises through 7days/ 24 hours such as flooding, riots, fire, and blackouts. There is also a Crisis Assessment Team (CAT) which is responsible for providing warnings about the crisis to various departments in the risk areas so that they can prepare to deal with the crisis in a timely and appropriate manner. Business Continuity Management (BCM) includes using nearby distribution centers to deliver products, transporting products using large trucks, using alternative routes, finding alternative products, and establishing temporary distribution centers. The Company has also collaborated with key suppliers who are strategic partner developing Business Continuity Plan (BCP) to ensure that products can be delivered during crisis to minimize the negative impact on the sales revenue. In addition, the Company has appropriately bought insurance to compensate for loss and to alleviate the cost burden that may occur in the future, covering distribution centers, stores and subsidiary companies. In 2024, the Company conducted scenario-based training exercises in the form of Simulation Tests and Table Top Tests for 4 corporate-level plans. Additionally, the Company elevated the standards of its ISO 22301-certified systems, which include the Bang Bua Thong Distribution Center, Suvarnabhumi Distribution Center, and Mahachai Distribution Center. In 2024, the Company expanded these standards to two additional distribution centers: the Khon Kaen Distribution Center and the Hat Yai Distribution Center. Through these measures, the Company is confident that all its distribution centers will maintain their capabilities with sufficient capacity and scale to support the expansion plans for both domestic and international branches, as well as future new business ventures. Furthermore, these centers will be able to integrate and function as a highly efficient backup distribution network, ensuring seamless operations and mutual support across the entire system. |
Sustainability Risk
4. Cyber Threats
| Impact | Likelihood | Risk Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Moderate | MM |
| Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|
| Operational changes from offline to online have introduced the company to additional cybersecurity risks almost all the time. Therefore, the company has set up to manage cybersecurity risks in order to continue with its operational plans. BCM: Business Continuity Management. This change may result in the risk of cyber threats. In Thailand, such cyber threats are regulated by various laws and regulations, including the Computer Crime Act, the Cyber Security Act and the Personal Data Protection Act. The Company recognizes the importance of having pre-emptive measures to handle cyber threats. Cyberattacks, such as theft of trade secrets or leakage of customers’ or employees’ personal information, can result in adverse financial impact,damage the Company’s reputation and credibility, or implicate the Company for failing to comply with the law. |
CP ALL has been regularly reviewing its corporate strategy and plans with internationally recognized data security experts. Additionally, the abovementioned data security experts collaborate with the Company’s information technology supervision committee to review persistently. The Company also arrange for an evaluation of security measures from outside agencies (BITSIGHT Security Rating Service) once a year. To manage effectively according to the National Institute of Standards and Technology’s cybersecurity framework, which comprises of five areas of how to deal with cyberattacks, including identification, prevention, detection, retaliation and recovery. CP ALL has also appointed a Chief Cyber Security Officer, responsible for all of CP ALL Public Company Limited’s information technology security. Furthermore, Gosoft (Thailand) Company Limited, a subsidiary of the Company, has been appointed to support the Company’s cybersecurity measures. It operates in accordance with international standards, and revises its policies to match with international standards, information security management system (ISO 27001), and privacy information security management system (ISO 27701). Both of which are international standards that deal with information technology security and management and Internet security strategies, the subsidiary works to ensure the Company’s business continuity and manage risks to fall within an acceptable range. Gosoft (Thailand) Company Limited is required to review the Company’s cybersecurity strategy annually. Additionally, the subsidiary works to promote cyber security awareness amongst employees and new hires through the onboarding program. This includes signing an acknowledgement of policies and practices.Additionally ensure that business partners are informed about secure data usage when connecting to the company’s IT system and customers educate on “Cyber Vaccine, Know the Tricks, Fight Online Threats” initiative, offering crucial alerts on safe online service usage and cybersecurity protection via social media channels. Furthermore, conduct training session and assessments including cyber crisis simulation programs such as the Cyber Security War Game, phishing campaigns, and Cyber Security Drill Test. The various channels offered, serve as a means to improve employee’s understanding of cybersecurity in order for them to safely and correctly work with such technology, and to be able to correctly deal with any cybersecurity threats that may occur in every quarter. |
Emerging Risk/Future Risk
9. The risk from transitioning into a completely aged society increases the demand for health products
| Impact | Likelihood | Risk Ranking |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate | Moderate | MM |
| Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|
|
CPALL has been actively managing health and nutrition products through various support programs and promoting research in health products internally and externally. However, with the transition into a completely aged society and the trend towards becoming a super aged society, CPALL needs to adapt and prepare to deliver products and services which can fulfill future needs. The effect and risk of losing opportunities in selling health products and the elderly group, which accounts for 12.88 percent of total sales compared to all food and beverage products sold in 7-Eleven stores, may also impact organizational direction-setting and strategy. Additionally, CPALL prepares to address the increased budget for research on products and services suitable for the elderly group by 46 percent (Baht 44 million), with the aim to increase health products by 25 percent. In 2024, the Ministry of Public Health announced policies to reduce chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs), which include high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, obesity, cardiovascular disease, etc., among the population. According to the National Statistical Office Health and Welfare Survey in 2023, Thailand found NCDs among people aged 60 years and over, with a 56.3 percent incidence of illness when compared to other age groups. To reduce new cases and promote sustainable health for Thai people, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) collaborates with network partners in both the public and private sectors, including the Ministry of Public Health, Institute of Nutrition Mahidol University, Health Promotion Support Office (Thai Health Promotion Foundation) and private food SMEs to promote and strive for food products with modified formulas which reduces sweetness, oil, and saltiness. The offered alternatives for consumers are identified by the symbol “Healthier Choice” as a means to help consumers notice and make consumption decisions more conveniently. Currently, products certified with the Health Choice Symbol cover 14 groups: main meals, beverages, condiments, dairy products, instant foods, snacks, ice cream, oils and fats, bread, breakfast cereals, baked goods, snack products, fish and seafood products, and meat products. The health alternative products identifiable with the symbol “Healthier Choice” may have an impact towards purchasing decisions among elderly people with NCDs. In addition, campaigns from the government sector have motivated the Company to source healthy products to fulfill the “Healthier Choice” category and meet demands for health-conscious product alternatives, especially among the elderly. Product manufacturers are required to apply for product registration with certification costs of 10,000 Baht per time per product and symbol renewal of 5,000 Baht per renewal per product by January 1, 2025, when the regulation comes into effect. Product manufacturers have to accept increased costs for product registration and certification, thus impacting supply chains and |
CPALL develops products through researching food innovations and continually increasing nutritional value in collaboration with CP Food Lab Co. Ltd., Product Development and Quality Assurance Office (PDQA) CP ALL Public Company Limited, and external organizations with expertise including the Thailand Institute of Scientific and Technological Research (TISTR) and the Department of Product Development, Faculty of Agro-Industry, Kasetsart University. The Company concurrently determines criteria for health products within the Company’s Private Brands in line with certification standards of external agencies and international standards. The Company aims to promote and support food and beverage product groups which reduce sugar, fat, sodium, additives inclusive of preservatives, food coloring, sweetener substitutes, antibiotics, etc. and product groups which increase nutritional value, including fortification with vitamin A, zinc, iodine, fiber, iron, etc. The Company has promoted CPRAM’s elderly food project which emphasizes the importance of health under the “Creator” brand. The brand focuses on foods with specific nutritional value and amount, food properties or raw materials conducive for chewing, digestion and absorption, nutrition suitability according to age, and high protein foods not specifically designed for the elderly. Customers can choose to eat “Creator” to gain complete nutrients while experiencing a “easy to chew, easy to digest” product with high nutritional value and good taste to fulfill the needs of the aging society in Thailand and globally. In addition to the food and beverage product group, the Company carefully selects quality raw materials from responsible sources for its products which contain Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) and ensures its certification and traceability. The Company has established a process to continuously monitor and review operating results to ensure continued promotion of health and well-being, and capabilities to fulfill the organization’s short-term and long-term goals. This process entails compiling a database for policy development, operation plans and various research plans in the future to support trends of changing products and services for the elderly group in the future. The service level has been elevated to cater to customer groups with difficulty visiting 7-Eleven stores through ordering products from the application ‘7App’ with delivery service. The elderly who are not comfortable accessing digital systems or customers without a smartphone or mobile internet can opt for CPALL’s new ordering service via the Call Center by dialing 1371. The Chat & Shop and Line OA services also facilitate ordering of various products in 7-Eleven stores. |
Internal control and risk monitoring mechanisms
The company continuously monitors, reviews, and evaluates its risk management processes through a control mechanism and risk monitoring.
Assessing high-risk activities
Selecting high-risk processes
Establishing risk control measures
Randomized assessment of control measures by auditors
Risk Management Process Audit
The Internal Audit Office is responsible for inspecting and evaluating operations according to risk reduction measures as a means to ensure operations are aligned with good corporate governance principles, including the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) internal control framework and the international standard for business continuity management ISO 22301: Business Continuity Management (BCM). The key objective is to manage the Company’s risks at an acceptable and manageable level.The Internal Audit Office is responsible for inspecting and evaluating operations according to risk reduction measures as a means to ensure operations are aligned with good corporate governance principles, including the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) internal control framework and the international standard for business continuity management ISO 22301: Business Continuity Management (BCM). The key objective is to manage the Company’s risks at an acceptable and manageable level.
In addition to internal audits, the company strengthened its international standards in 2024 by receiving business continuity management certification (ISO 22301: BCM) for two additional locations: the Khon Kaen and Hat Yai Distribution Centers. Furthermore, our risk management process was audited by LRQA, an independent external firm, to ensure its effectiveness and compliance with international standards.

CPALL ISO 22301 Certificate for Bangbuathong (CDC ) 
CPALL ISO 22301 Certificate for Head Office 
CPALL ISO 22301 Certificate for Mahachai (DC )
Ongoing Project: Risk Management and Business Continuity Management Training Program for Risk Champion
The Risk Management unit, in collaboration with Panyatara Co., Ltd. and All Training Co., Ltd., organizes the online training course “Risk Management and Business Continuity for Risk Champion 2024”. The training objective includes skills development, new learning experiences applicable as guidelines for risk management within the CP ALL business group, and increased capability to evaluate organizational risk management according to the Risk Score criteria. Project participants will undergo post-training assessments to verify comprehension and enhance awareness of processes to determine risks and subsequent prevention methods to ensure continuous and uninterrupted operations. Over 317 Risk Champions from the CP ALL business group participated this year.
Ongoing Project: Black Swan Search continuation
The Company has continued the Black Swan project for the 11th consecutive year to raise awareness of risks for the Company’s personnel. Management and employees are encouraged to take part in identifying enterprise risks that could potentially impact the Company’s operations and goals through the submission of risk topics in a contest available at various channels. The risks topics are related to the below 6 issues, as follows:

Continuous Business Operations
Work Process
Products and Services

Outsources Hiring
Corporate Sustainability
Activities Related to the Company’s Subsidiaries
The awarded risk issues will be considered for further development of appropriate support measures and management strategies to effectively implement them. In 2024, there were a total of 1,460 risk issues submitted by employees for competition. The top five risk issues with the highest number of submissions are: 1.)Health and Safety Risks 2.) Cybersecurity Risks 3.) Environmental Risks 4.) Customer Service Risks 5.) Regulatory Compliance Risks .
Furthermore, the Company conducts Risk Score evaluations to measure the overall risk management effectiveness of each department. The Company welcomes suggestions for further development and improvement of risk management systems in all areas to enhance efficiency. This covers over 80 departments on a quarterly basis, along with providing guidance and knowledge exchange through online systems. Additionally, exemplary risk management practices are showcased to elevate capabilities through the Risk Score Clinic project weekly. Departments demonstrating consistent excellent performance will be publicly acknowledged by the Chief Risk Officer and the CEO as role models for the organization, fostering pride among the department’s risk management personnel.
Emerging Risks
The Company considers risks toward business operations important, thus, measures and guidelines for management and administration have been established to promptly respond to risks. This includes regular annual reviews of issues and various trends to analyze new risks which may affect business operations. Moreover, the Company can identify 3 new risks and analyze the impact of these risks
on business operations, along with outlining preliminary management measures and guidelines as follows:
Risks from rapid changes in Generative 1 AI technology in the e-Commerce business
Online sales trends in 2024 include increased utilization of Generative AI technology in e-commerce businesses, specifically through Live Commerce and Cross-border e-Commerce, Chinese products increasingly penetrate the Thai market with predictions of new e-Commerce players contending established players. The anticipated new player, an overseas online shopping platform which focuses on cheap products, could fuel growth potential in the Thai e-Commerce market where growth is expected at 19% according to Google’s Southeast Asia Digital Economy Report summary last year. The robust growth resulted in CP ALL’s e-commerce business growth reaching 11% of total sales.
However, the integration of Generative Al technology will most likely impact new investment projects, investments in subsidiaries and distribution centers, and lead to more business operations within group companies in a manner which preserves and creates a good service experience at 7-Eleven stores in a sustainable way.
The rapid introduction of Generative AI technology in the e-Commerce business has impacted new investment projects, investment in subsidiaries and distribution centers in CP ALL’s group business operations. It helps maintain and create sustainable customer experiences at 7-Eleven stores. In 2024, investments will account for approximately 31% of the total 13,000 million Baht budget. In the scenario where Generative Al technology is introduced and fully adopted as an aid in analyzing products and services for consumers within the next 3-5 years, a significant increase in investments can be observed in new projects, subsidiaries, and distribution centers. Examples of potential investments include developing work processes throughout the value chain at branch stores, at warehouse systems, and at support units within the head office to enhance the purchasing experience throughout all channels, AI Ordering to replenish inventory appropriately according to various situations and environmental factors. The developments mentioned increase the average revenue per store per day and sustainably maintains good customer experience for 7-Eleven store patrons in the future.
CP ALL aims to invest in Generative Al technology as a tool to assist in analyzing product and service needs of individual customers. This approach which identifies products or product categories customers are personally interested in (Personalization) to be appropriately selected and ordered (AI Ordering) while taking into account various situations and environmental factors, yielded an increased average revenue per store per day of approximately 6-7%. Other developments include initiating communication channels with the diverse customer base while considering customer communication behavior, especially via online channels through popular social media comprising TikTok, Instagram, X (Twitter), Line, YouTube and Facebook, including live streaming. The in-depth analysis targets and recognizes customer needs quickly and accurately though technological applications to enable product and service presentation which satisfies customer requirements in the future.
CP ALL closely monitors Generative Al technology advances which affect the Company’s business strategy through defining business strategy, focus on growth from current strengths, and responses to new living norms and the digital society. In managing the changing trends and improving formats for good customer experience, the Company has introduced new products, sales promotions in conjunction with the signature service of employees within the store who double as product organizers and product deliverers, etc. The interactions create customer bonds and trust and allow store employees to understand customer needs, thus building capabilities to provide offerings which align with customer requirements. Interactions encompass the various customer contact points, channels to product and service, services through branch stores, vending machines, and online platforms. The online platforms include 7Delivery, an on-demand delivery service, and All Online which represents a department store near home. The mentioned strategy has received consistently good customer response, especially at branch stores where foreign tourists often frequent.
The risk from transitioning into a Completely Aged Society increases the demand for health products
Thailand is transitioning into a Completely Aged Society, according to data from the Department of Provincial Administration, Ministry of Interior, in 2023. It was found that Thailand has a population of people aged 60 and above, or the elderly, accounting for 1 in 5 (13 million people) of the total population (66 million people), with a continuous upward trend projected over the next 5-10 years. It is estimated that Thailand will evolve into a Super Aged Society, with the elderly population increasing to 28% of the total population. This will directly impact the demand for health-related products and services, resulting in greater need for healthfocused food products, functional foods, and foods with modified ingredients. This trend may influence CP ALL’s strategies, budget planning, research in product and service development, as well as procurement of health-enhancing products.
CP ALL has been actively managing health and nutrition products through various support programs and promoting research in health products internally and externally. However, with the transition into a Completely Aged Society and the trend towards becoming a Super Aged Society, CP ALL needs to adapt and prepare to deliver products and services which can fulfill future needs. The effect and risk of losing opportunities in selling health products and the elderly group, which accounts for 12.88% of total sales compared to all food and beverage products sold in 7-Eleven stores, may also impact organizational direction-setting and strategy. Additionally, CP ALL is preparing to respond by increasing its budget for research on products and services suitable for the elderly. The budget has been raised to 44 million Baht, an increase of 42% compared to 2023, to support the procurement of health-related products by 25%.
In 2024, the Ministry of Public Health announced policies to reduce chronic non-communicable diseases (NCDs), which include high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol, obesity, cardiovascular disease, etc., among the population. According to the National Statistical Office Health and Welfare Survey in 2023, Thailand found NCDs among people aged 60 years and over, with a 56% incidence of illness when compared to other age groups. To reduce new cases and promote sustainable health for Thai people, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) collaborates with network partners in both the public and private sectors, including the Ministry of Public Health, Institute of Nutrition Mahidol University, Health Promotion Support Office (Thai Health Promotion Foundation) and private food SMEs to promote and strive for food products with modified formulas which reduces sweetness, oil, and saltiness. The offered alternatives for consumers are identified by the symbol “Healthier Choice” as a means to help consumers notice and make consumption decisions more conveniently. Currently, products certified with the Health Choice Symbol cover 14 groups: main meals, beverages, condiments, dairy products, instant foods, snacks, ice cream, oils and fats, bread, breakfast cereals, baked goods, snack products, fish and seafood products, and meat products The health alternative products identifiable with the symbol “Healthier Choice” may have an impact towards purchasing decisions among elderly people with NCDs.
In addition, campaigns from the government sector have motivated the Company to source healthy products to fulfill the “Healthier Choice” category and meet demands for health-conscious product alternatives, especially among the elderly. Product manufacturers are required to apply for product registration with certification costs of 10,000 Baht per time per product and symbol renewal of 5,000 Baht per renewal per product by January 1, 2025, when the regulation comes into effect. Product manufacturers have to accept increased costs for product registration and certification, thus impacting supply chains and CP ALL. The expected increase in product cost amounts to 10-15 million Baht accounts for costs forwarded to good health and well-being food, and other food and beverage groups.
CP ALL develops products through researching food innovations and continually increasing nutritional value in collaboration with CP Food Lab Co. Ltd., Product Development and Quality Assurance Office (PDQA) CP ALL Public Company Limited, and external organizations
with expertise including the Thailand Institute of Scientific and Technological Research (TISTR) and the Department of Product Development, Faculty of Agro-Industry, Kasetsart University. The Company concurrently determines criteria for health products within the Company’s Private Brands in line with certification standards of external agencies and international standards.
The Company aims to promote and support food and beverage product groups which reduce sugar, fat, sodium, additives inclusive of preservatives, food coloring, sweetener substitutes, antibiotics, etc. and product groups which increase nutritional value, including fortification with vitamin A, zinc, iodine, fiber, iron, etc. The Company has promoted CPRAM’s elderly food project which emphasizes the importance of health under the “Creator” brand. The brand focuses on foods with specific nutritional value and amount, food properties or raw materials conducive for chewing, digestion and absorption, nutrition suitability according to age, and high protein foods not specifically designed for the elderly. Customers can choose to eat
“Creator” to gain complete nutrients while experiencing a “easy to chew, easy to digest” product with high nutritional value and good taste to fulfill the needs of the aging society in Thailand and globally.
In addition to the food and beverage product group, the Company carefully selects quality raw materials from responsible sources for its products which contain Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs) and ensures its certification and traceability. The Company has established
a process to continuously monitor and review operating results to ensure continued promotion of health and well-being, and capabilities to fulfill the organization’s short-term and long-term goals. This process entails compiling a database for policy development, operation plans and various research plans in the future to support trends of changing products and services for the elderly group in the future. The service level has been elevated to cater to customer groups with difficulty visiting 7-Eleven stores through ordering products from the application ‘7App’ with delivery service. The elderly who are not comfortable accessing digital systems or customers without a smartphone or mobile internet can opt for CP ALL’s new ordering service via the Call Center by dialing 1371. The Chat & Shop and Line OA services also facilitate ordering of various products in 7-Eleven stores.
The Risk of Failing to Achieve Net Zero Target due to Scope 3 emissions
CP ALL assigned the Sustainability Development Subcommittee to oversee climate change management and specialized operations teams for instance, teams to manage energy efficiency and energy conservation, the solar installation team, environmentally friendly packaging development team, etc. The subcommittee performs administrative duties related to managing climate change under the strategy “7 Go Green”, which focuses on reducing greenhouse gas emissions from business operations to meet stipulated targets. With aims for carbon neutrality (Carbon Neutral) by 2030 and net zero greenhouse gas emissions (Net Zero Emission) by 2050, greenhouse gas management is divided into 3 categories: direct greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 1), indirect greenhouse gas emissions from energy usage (Scope 2), and other indirect greenhouse gas emissions (Scope 3). The Company has considered establishing goals to reduce the organization’s greenhouse gas emissions to net zero through a validation process according to the guidelines of the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi). In addition, the Company has established a framework for operations and guidelines to conduct business responsibly in terms of climate change throughout the supply chain in alignment with Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) guidelines with climate change information disclosures (IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures).
Achieving the stipulated goal is critical as the majority of the Company’s greenhouse gas emissions come from other indirect activities (Scope 3) arising from activities within the supply chain, inclusive of greenhouse gas emissions occurring from production processes of intermediary products used by the Company, internally produced products, transportation, distribution, product utilization and garbage disposal. The mentioned processes account for the highest proportion of greenhouse gas emissions, reaching 88% of all greenhouse gases or equivalent to 13,030,541 tCO2e in 2030.
Achieving the established climate goals affects business practices within CP ALL’s supply chain whereby the Company aims for both small and large suppliers to adapt to a low-carbon society. In adopting low-carbon measures, production processes are modified and the cost of production increases. Smaller suppliers are confronted with limitations in collecting and reporting greenhouse gas emissions data thus requiring additional financial support and knowledge from the Company. CP ALL’s internal operations require investment in additional projects to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, including employee transportation modifications and waste management, etc. which contributes to an overall business operating costs of 8,976 million Baht. Successful adoption of this initiative not only requires Company commitment but also stakeholder cooperation and their varying capabilities. The inability to proceed accordingly may impact the realization of goals and affect corporate image in the form of “greenwashing” accusations and potential societal resistance in the future, etc.
CP ALL is committed to operating under sustainability strategies covering the dimensions of good governance and economics, society and the environment, including: 7 Go Green, 7 Go Together and 7 Go Right strategies. In risk assessments of material impacts toward all
stakeholder groups, encompassing positive and negative impacts in reducing greenhouse gas emissions from suppliers, CP ALL has established a policy and manual for sustainable procurement used to select and promote business suppliers. Instance of policies include sourcing from sustainable agriculture and utilizing environmentally friendly products, etc. To reduce greenhouse gas emissions generated by suppliers, the Company established initiatives and prepared capacity assessments and supplier readiness assessments for low-carbon society adoption appropriate for each supplier group. For instance, two events to enhance awareness and basic knowledge on reducing greenhouse gas emissions for small suppliers were organized in 2024. Incentives were provided to suppliers who cooperate with the Company in driving the country’s greenhouse gas emissions reduction goals, etc.
CP ALL has invested in developing the production systems in addition to managing and reducing waste within business operations, a means to reduce indirect greenhouse gas emissions associated with the Company. Executives involved in overseeing the Company’s sustainability policy are tasked with regularly monitoring developments regarding missions of Thailand Carbon Neutral Network (TCNN) and the Global Compact Network of Thailand (GCNT). Awareness of updates keeps the Company informed of trends, including participation in expressing opinions and driving forward the agenda for climate change management at the national level, modifying organizational policies consistent with national policies, as well as allowing the organization’s business activities to proceed continuously while taking into account the positive and negative impacts on all relevant stakeholder groups.
Managing cyber security and data protection
In tandem with standards adoption, the Company has conducted a cyber threat risk assessment in accordance with international guideline NIST (Cyber Security Framework). The guidelines are reviewed in conjunction with business goals and the current environmental situation to determine the most appropriate information technology systems security policies and appropriate application which considers personnel, processes, and technology through various projects as follows:
Ongoing Projiect: Cyber Security
In the digital era, where businesses increasingly rely on online systems, cybersecurity has become a critical priority. The Company constantly face cyber threats and must implement proactive measures to mitigate risks. To address this challenge, the company has planned and implemented comprehensive security measures across all dimensions, including training employees to raise awareness of cyber threats, strengthening cybersecurity protection systems, and ensuring that software is continuously updated to remain effective against emerging threats.
Cultivating an organizational culture with cybersecurity wellness
Cyber Hygiene Culture
Control cyber security standards
Cyber Assurance

Operations for surveillance and cyber threat prevention
Cyber Operation
In 2024, the Company underwent cyber security assessments and ratings from BITSIGHT Security Rating Service, a third-party organization which analyzes cyber security levels and corporate cyber. Through utilizing the Security Ratings scoring method and continuous assessment to measure cyber security level for listed companies and securities companies (Cybersecurity Resilience Survey 2024), Cybersecurity Levels which reflect management, data administration, and cyber security are determined. Enhanced security levels promote credibility and corporate image thus the Company proceeds according to the following important guidelines:
Impacts and Benefits

of the Company’s network information systems comply with the Information Security Management System (ISO 27001) certification through installations

of employees passed the Phishing Simulation Test

of employees working in cyber security systems (33 people) passed training and knowledge testing on cyber security topics

of Company internet network systems and websites have undergone Vulnerability Assessment by a third-party company and the internal system hacking expert unit (Red Team), with results considered in future improvements by the operating team to enhance security
Personal Data Protection Management
The Company is cognizant of the importance of data privacy, a key privacy right upheld by the Constitution of the Kingdom of Thailand and the principles of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. In an approach to increase confidence among stakeholders throughout the value chain, supervision is provided as follows:
Ongoing Project: Raising Awareness of Personal Data Protection
The Company is committed to raising awareness regarding personal data protection among employees at all levels through adhering to guidelines established in the organization’s key strategies and plans as an approach to reducing risks which may occur to the Company.
In 2024, the Company implemented steps to raise the level of personal data protection to international standards. The details are as follows:
Impacts and Benefits

of activities managing personal data comply with the Personal Data Protection Act

of employees passed PDPA guidelines training and knowledge assessment
of respondents exercised the rights of personal data owners within the specified time

serious grievances reported

in value of the damage caused by personal information leaks or violations
Other Information
Sensitivity Risk
1.Business Environment Risk
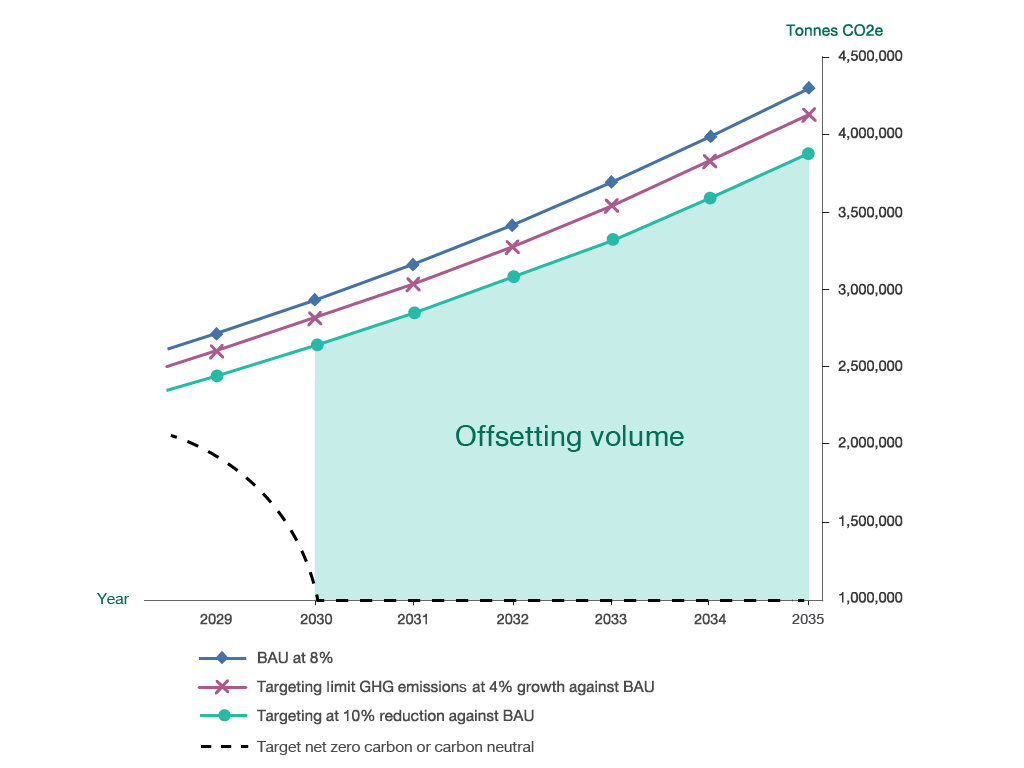
According to business expansion continuously, the Company is aware of development of GHG emissions reduction initiatives for various operations, including research, pilot projects, and applied to the business as well as collaboration program with stakeholders thought value chain. Under continuously development principle, the Company has preliminary studied on advance sustainability targets, being a carbon neutral organization or net zero carbon 2030 afterward. The Company has simulated 3 GHG emissions reduction scenarios (shown in diagram 1) which all cases are linked with the business growth. Additionally scenario has been performed by limiting volume of carbon offsetting at 20% of projection BAU case in 2030. The offsetting cost of all remaining carbon emissions will be used for range determination.
Results are indicating cost that associated climate change mitigation and linkage with business case which reflect effort and preparations required for co-mitigating the global issue.
Diagram 1 GHG emissions and carbon offsetting
| Data Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|
| (inputs and factors used for the analysis) | ||
| Voluntary Emission Reduction | 42.72 | Euro / tonne |
| Exchange rate | 38.37 | Bath / Euro |
| Carbon emissions forecasting 2030 (CEF2030) | 3,042,632.71 | tCO2e |
| Target limited GHGs growth at 4% | 2,086,322.77 | tCO2e |
| Target GHG reduction at 4.2% each year | 1,764,726.97 | tCO2e |
| 1% of revenue 2020 | 5,465.90 | MTBH |
Table 1: Sensitivity analysis for carbon offsetting on target year 2030 scenario
| Unit (million THB) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon pricing valuation | -10% | -5% | +-0% | +5% | +10% |
| Carbon emission (CEF2030) | 4,488.64 | 4,738.01 | 4,987.38 | 5,236.75 | 5,486.12* |
| Targeting Limit GHG emission at 4% growth against BAU | 3,077.85 | 3,248.84 | 3,419.83 | 3,590.82 | 3,761.81 |
| Target GHGs reduction at 4.2% each year | 2,603.41 | 2,748.05 | 2,892.68 | 3,037.32 | 3,181.95 |
* exceeded threshold at 1% of revenue
2. Compliance Risk and Operation Risk
Sensitivity Analysis of Future Salary Growth and Employee Turnover Rate
| Consolidated Financial Statements | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% increases in assumption | 1% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | |||||||
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| At 31 December | (in million Baht) | |||||||||||
| Future Salary Growth | 488 | 570 | -436 | -509 | 1,464 | 1,710 | -1,308 | -1,527 | 2,440 | 2,850 | -2,180 | -2,545 |
| Employee Turnover Rate | -781 | -928 | 952 | 1,143 | -2,343 | -2,784 | 2,856 | 3,429 | 3,905 | -4,640 | 4,760 | 5,715 |
| Separate Financial Statements | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% increases in assumption | 1% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | |||||||
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| At 31 December | (in million Baht) | |||||||||||
| Future Salary Growth | 247 | 300 | -221 | +268 | 741 | 900 | -663 | -804 | 1,235 | 1,500 | -1,105 | 1,340 |
| Employee Turnover Rate | -463 | -565 | 595 | 728 | -1,389 | 1,695 | 1,785 | 2,184 | -2,315 | -2,825 | 2,975 | 3,640 |
3.Market Risk
Sensitivity Analysis of Discount Rate
| Consolidated Financial Statements | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% increases in assumption | 1% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | |||||||
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| At 31 December | (in million Baht) | |||||||||||
| Discount Rate | -453 | -527 | 518 | 603 | -1,359 | -1,581 | 1,554 | 1,809 | -2,265 | -2,635 | 2,590 | 3,015 |
| Separate Financial Statements | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1% increases in assumption | 1% decrease in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 3% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | 5% increases in assumption | |||||||
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| At 31 December | (in million Baht) | |||||||||||
| Discount Rate | -223 | -273 | 254 | 311 | -669 | -819 | 762 | 933 | -1,115 | -1,365 | 1,270 | 1,555 |
Regular risk management education for all non-executive directors
Training Non-Executive Directors on risk management is pivotal to strengthening an organization. A deep understanding of risk management enables the board to effectively oversee operations, monitor and assess potential risks, and make strategic decisions based on risk information. In 2026, the company invited external experts to provide training to Non-Executive Directors on sustainability trends, risk challenges, and their impact on CP All Public Company Limited. All Non-Executive Directors participated in this training.

Financial incentives which incorporate risk management metrics
CPALL to enhance an effective risk culture throughout the organization, KPIs are linked to senior executives of the risk function and the performance of each KPI will be applied during the evaluation process. Part of senior executive’s incentive will be assessed by considering the evaluation result. KPIs that are used for performance evaluation of risk function are separated as follows:
– Dissemination of departmental risk management policies (Score 10%)
– Arrangement of internal risk reviews and reporting (Score 30%)
– Revision and improvement of BCM plan and BCM Team list (Score 25%)
– Ushering intra-agency participation in discovery for hidden corporate threats (Score 20%)
– Participation in risk management activities established by the Company (Score 15%)
Corporate KPIs related to risk management have been cascaded down from senior executives to line managers. Similar to senior executives, performances under these KPIs are linked to annual merit increase.
Incorporation of risk criteria in the development of products and services
CPALL values the integrity and safety of our products and services for consumers and customers. Integrating risk management practice into company-wide has become a corporate culture, Therefore, risk criteria have been incorporated into the product development and approval process. In addition, regulatory risks, product quality and safety, and product quality assurance risks are integrated into the product selection process via the “Pre-Audit Supplier” tool. The QA department will use the tool to assess the facilities, production potential, and product development of the new private brand suppliers.

